PET CT & Nuclear Medicine
What is PET CT & Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear medicine is an imaging modality used in radiology that involves the use of radioactive isotopes in the form of radiopharmaceuticals to diagnose and treat certain disease processes. It is most commonly used for evaluation of the heart, liver, lungs and bones, but it is also used to evaluate kidney function, the brain, thyroid and skin.
What are the benefits of PET scan?
In addition to imaging, nuclear medicine technology can also use the localization ability of radiopharmaceuticals to treat certain diseases like cancer and to provide pain relief for cancer patients.
What are the side effects?
Typically, there are no side effects of these radiopharmaceuticals to the patient.
How does it work?
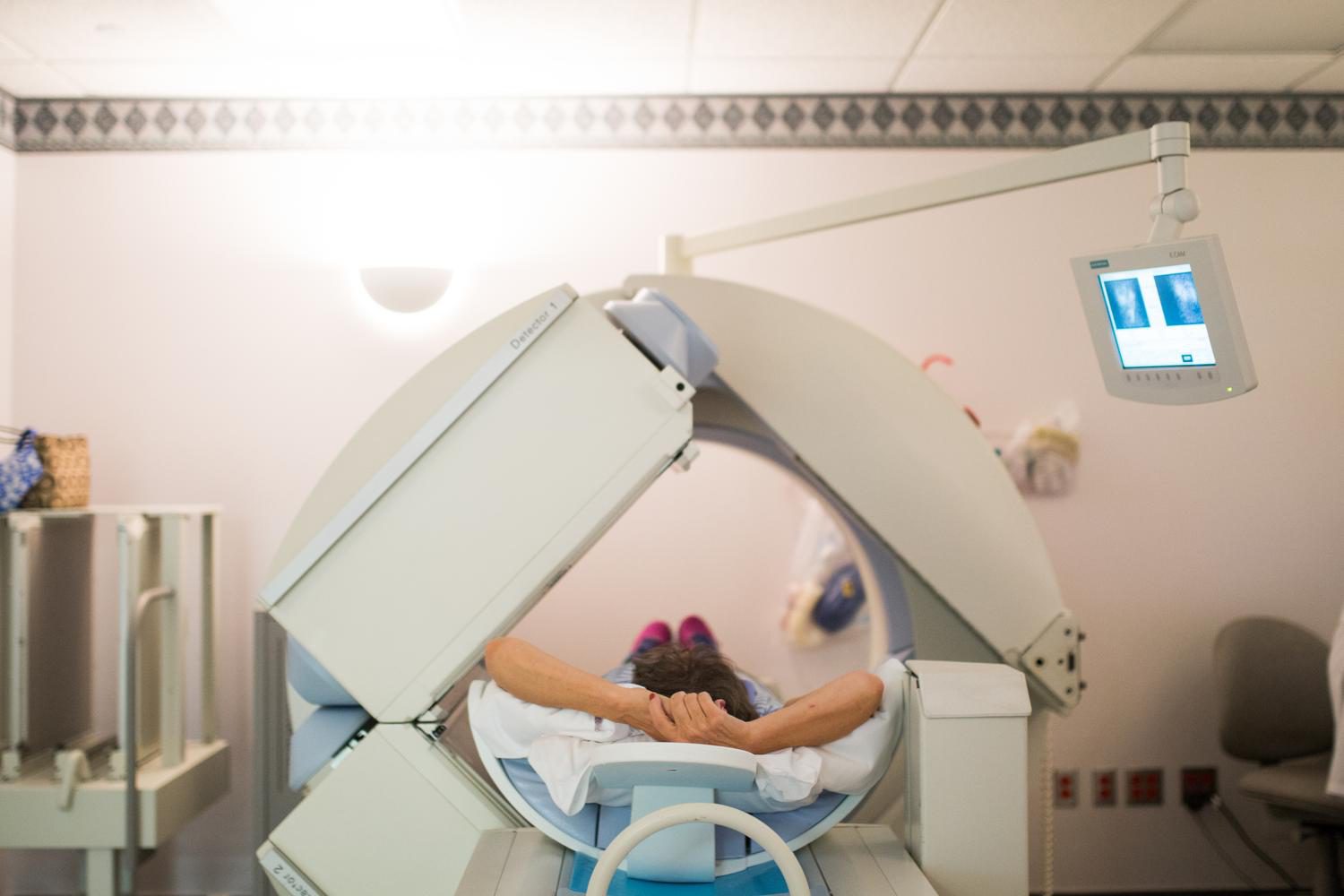
The radiopharmaceuticals will localize to specific areas in the body, allowing the radiologists who interpret these nuclear medicine studies to determine the extent of the disease based on physiology rather than only physical changes in the tissue. The administration of the radiopharmaceutical may involve ingestion, injection or inhalation of the material. This makes the patient the source of radiation and not an external device that will send X-rays through the patient.
Once administered, the patient will be imaged on a device called a “gamma camera,” which collects the emitted radiation to form a picture. In essence, the nuclear medicine picture is much like that of a newspaper as it contains many dots; each dot representing a radiation event. These pictures are often of a longer duration as they collect that radiation.
Find an Imaging Location Near You
Physician’s order required for services.
Quality & Safety
Innovation
Nuclear medicine/PET, like most healthcare technologies, is always growing and evolving. Many innovations have developed over the past few years, expanding nuclear medicine’s scope of practice:
Patient Rights
American College of Radiology
You have the right to submit comments regarding this facility’s radiology imaging and treatment services.
Submit your comments in writing and send to the facility or to the following address:
American College of Radiology
Attn: Accreditation Program Patient Comments
1891 Preston White Dr.
Reston, VA 20191-4326

