Skin Cancer
St. Elizabeth Healthcare takes a team approach to screening, diagnosing and treating skin cancer. Our primary care doctors, dermatologists and cancer treatment specialists work together to detect skin cancer early. We create personalized treatment plans for the best possible outcomes.
- Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. More people are diagnosed with skin cancer than all other cancers combined.
- Skin cancer is treatable if detected early. When found early, the 5-year survival rate for melanoma is 99%.
- The most important thing you can do to reduce your risk of skin cancer is to protect yourself from the sun and have your skin checked annually.
What You Should Know About Skin Cancer
Your skin is your largest organ — it covers and protects your entire body. However, it is vulnerable to damage from the harmful rays of the sun. When non-melanoma skin cancers are found early, they are very treatable. Melanoma is a more aggressive skin cancer. It accounts for 3% of all skin cancers.
Types of skin cancer include:
Make an appointment
For more information, please contact your oncologist or the Cancer Care Center at (859) 301-4000.
Preventing Skin Cancer
Protecting your skin from the sun’s UV rays will reduce your risk of skin cancer. The experts at St. Elizabeth Healthcare also recommend an annual skin check to find suspicious spots or changes to your skin. Other ways to prevent skin cancer include:
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Avoid the strongest rays of the sun between the hours of 10 a.m. and 2 p.m.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours.
- Wear sun-protective clothing.
- Wear a broad-spectrum, water-resistant sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Causes of Skin Cancer
Most skin cancers are caused by previous sun exposure. Protecting your skin is the first line of defense. Anyone can get skin cancer, but risk factors for developing it include:
- Blond or red hair.
- Blue or green eyes.
- Family history of skin cancer.
- Light skin tone.
- Older age.
- Personal history of skin cancer.
- Skin that sunburns easily.
- Skin with a lot of freckles or moles.
If you have a personal history of skin cancer, we make sure you have access to our specialists so any recurrences can be caught early, when skin cancer is most treatable. Our dermatologists are available to evaluate your skin, and you can send photos of any spots or patches you’re concerned about through our secure MyChart patient portal.
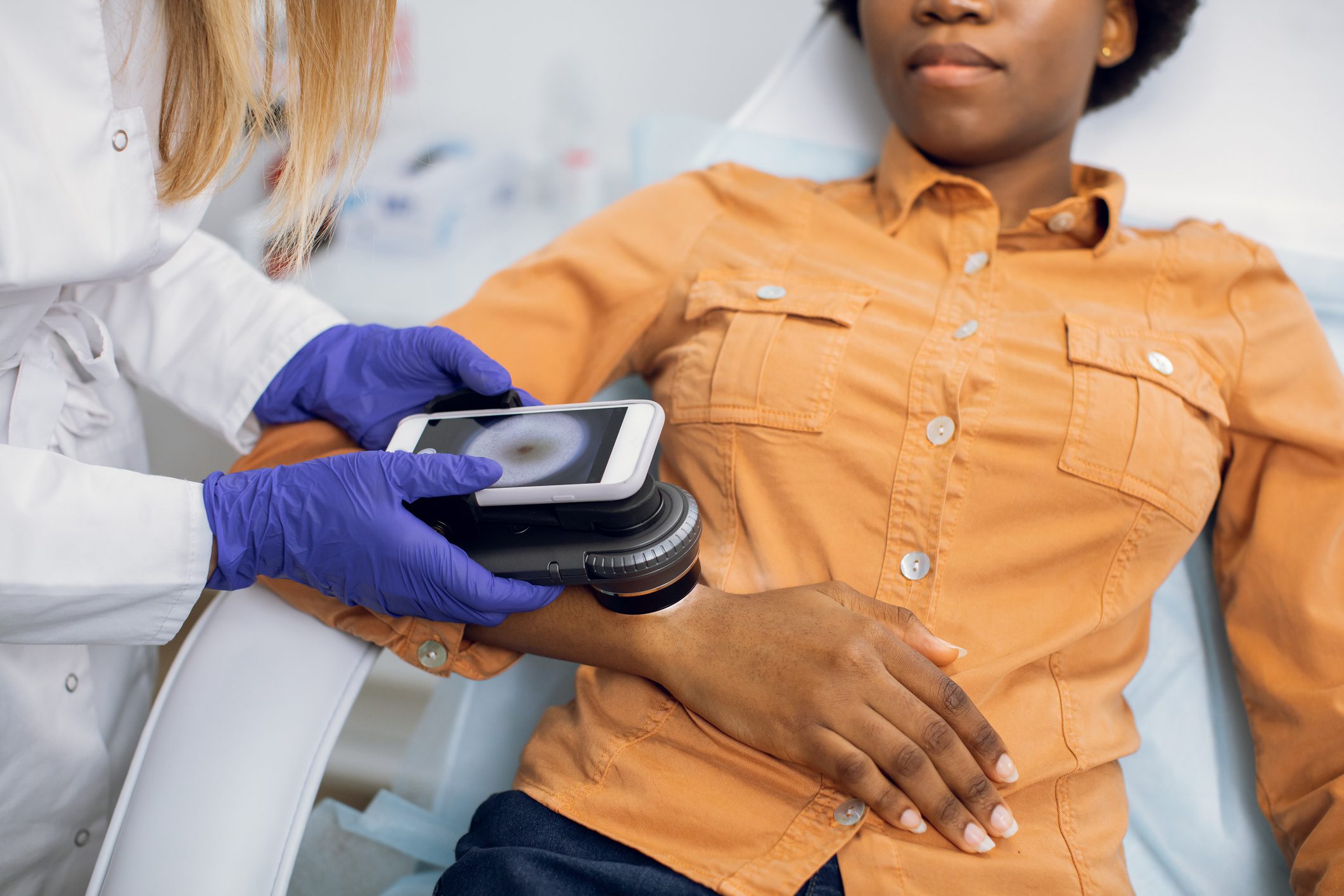
Skin Cancer Screening
Routine screenings are an important tool in detecting skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. It’s important to be familiar with your skin so that you notice any new spots, spots that are different from others, or spots that are changing, itching or bleeding.
St. Elizabeth Healthcare partners with Melanoma Know More , a community program based in Cincinnati that provides education about melanoma. Melanoma Know More provides free skin-check screenings.
Our experts recommend that you do a skin check at home each month. To do a skin check, look at the front and back of your body, using a mirror as necessary. Look for changes in the skin and moles that could indicate melanoma. Remember the ABCDEs of melanoma:
Genetic Testing for Skin Cancer
We believe in a proactive approach to detecting skin cancer. If you have a family history of cancer or are concerned about your risk, genetic counseling is an option to consider. Genetic counseling provides important information to you and your family about cancer risk and risk reduction and prevention. A blood test can show genetic mutations that may put you at higher risk for developing skin cancer. If your DNA shows you are at risk, we will recommend a more rigorous screening schedule, including additional blood work or PET/CT scan to identify skin cancer as early as possible.
For patients diagnosed with skin cancer, our hereditary cancer program offers information and resources on inherited disease. Genetic testing can help determine how a cancer will respond to treatment — and allow us to develop a laser-focused treatment plan specific to your cancer cells’ anatomy.
Skin Cancer Diagnosis
If your primary care doctor or dermatologist finds a suspicious spot on your skin, you may need a biopsy. A biopsy removes some tissue from the affected area and tests to see if it’s cancerous and what type of skin cancer. Types of biopsies include:
The pathologists who analyze your tissue sample are dermatopathologists — pathologists who specialize in diseases of the skin. If your biopsy reveals cancer, we may run more tests to make sure it hasn’t spread.
Skin Cancer Treatments
At St. Elizabeth Healthcare, we believe in caring for you, not just treating your cancer. Our holistic approach means we integrate cancer treatment with care to minimize side effects and help you manage the symptoms that may occur with treatment. Our goal is to make you as comfortable as possible and give you the best quality of life while we use innovative approaches to treat your cancer.
We have a team of doctors that reviews every skin cancer diagnosis. This team — which includes medical oncologists specializing in immunotherapy and precision medicine, surgical oncologists, radiation oncologists, neurosurgeons, plastic surgeons, genetic counselors, pathologists, nurses and support staff members — creates a treatment plan that is just right for you.
Your treatment plan may include:
Treating Advanced Stage Melanoma
At St. Elizabeth, our medical oncologists work with doctors from across the health system to create a customized treatment plan for melanoma that has spread to other parts of your body. Our physicians are experts in immunotherapy and targeted molecular therapies that use your DNA to specifically target cancer cells. We are committed to offering our patients the latest treatment options, including access to cutting-edge clinical trials
Our nurse navigator will help you understand your diagnosis, schedule appointments and guide you every step of the way.
Skin Cancer Surveillance
When you’re diagnosed with skin cancer, you have to remain vigilant. Your care does not end when active treatment is finished. We want to make sure your cancer doesn’t come back — and if it does, we want to make sure we catch it early.
After your cancer is cured, we will continue to see you every three months until we feel yearly monitoring would be safe. Routine screening is a proven method to detect cancer early.
We encourage you to send us pictures of any suspicious spot through our secure online patient portal, MyChart. We may also use more advanced technologies such as blood testing and PET/CT scans to monitor for any recurrence.
Your Skin Cancer Care Team
Dr. Kristen Ahern
Dermatology
Dr. Christina Alexander
Dermatology
Lauren Butler, PA-C
Dermatology
Dr. Daniel Flora
Oncology
Dr. Joseph Guenther
General Surgery
Dr. Jordan Jones
Dermatology
Dr. Jason Martin
Dermatology
Kaitlin Pielage, APRN
Oncology
Dr. Pratish Shah
Radiation Oncology
Dr. Nneka Udechukwu
Dermatology
Dr. Nicole Warner
Dermatology, MOHS Surgery
Dr. Jonathan Webster
Dermatology
Dr. Brent Xia
Surgical Oncology