X-Ray
What is X-Ray (Routine Radiology)?
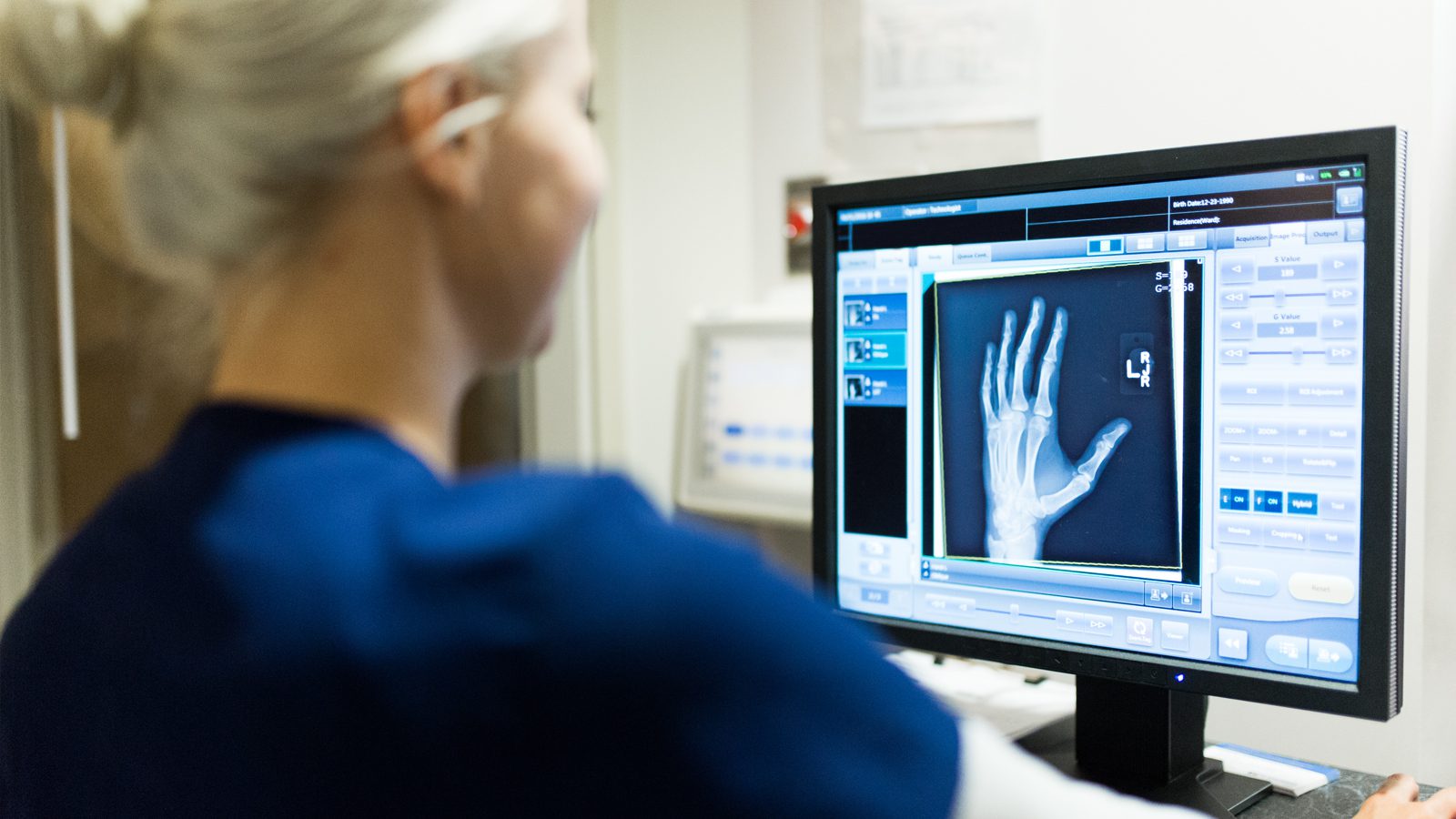
Routine Radiology (X-ray) is an excellent diagnostic tool for the evaluation of the skeletal, chest and gastrointestinal systems. The density of bone is not easily penetrated by X-ray; therefore the evaluation of the skull, spine, ribs, pelvis and upper and lower extremities are readily identified.
When are X-Rays used?
X-rays must be ordered by a physician, chiropractor, dentist, physician assistant or nurse practitioner licensed to prescribe. Due to the radiation exposure, X-ray can only be administered by a licensed radiographer.
There are three different “forms” of X-ray: skeletal, chest and gastrointestinal.
Find an Imaging Location Near You
Physician’s order required for services.
Barium sulfate, air and iodine are effective in profiling hollow organs and veins. These tests are useful in diagnosing achalasia, diverticula, hiatal hernia, ulcers, gastritis, pyloric stenosis, tumor and obstruction and other possible conditions.
How are X-ray images taken?
X-ray film was utilized for many years to acquire a “hard copy” of images. Today, with enhanced technology, X-ray images are digital and can be diagnosed, reviewed and stored electronically through computers. This technology allows your medical record to be forwarded to any facility within a network. Routine X-ray procedures of the skeleton and chest can be performed without an appointment. Gastrointestinal X-rays require an appointment through Central Scheduling and, in some cases, a “prep” to be taken by the patient prior to examination.
Quality
St. Elizabeth Healthcare’s professional radiographers are all licensed by the State of Kentucky and certified by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists.
Safety
At St. Elizabeth Healthcare, we subscribe to the “Image Gently” and “Image Wisely” philosophies. This means we are dedicated to providing the highest quality images, infant to adult, at the lowest radiation dose achievable.
Innovation
St. Elizabeth Healthcare Routine Radiology utilizes both computed radiography (CR) and digital radiography (DR). Computed and Digital Radiology both use a lower dose of radiation than conventional film to obtain an image and compute it into a readable image for a physician to diagnosis and treat patients. DR is a directly captured image, where CR must first be processed. Both are high quality and are then digitally stored on our Picture Archiving Communication System (PACS). Images are readily available to any healthcare facility or physician within the network.
Patient Rights
American College of Radiology
You have the right to submit comments regarding this facility’s radiology imaging and treatment services.
Submit your comments in writing and send to the facility or to the following address:
American College of Radiology
Attn: Accreditation Program Patient Comments
1891 Preston White Dr.
Reston, VA 20191-4326

